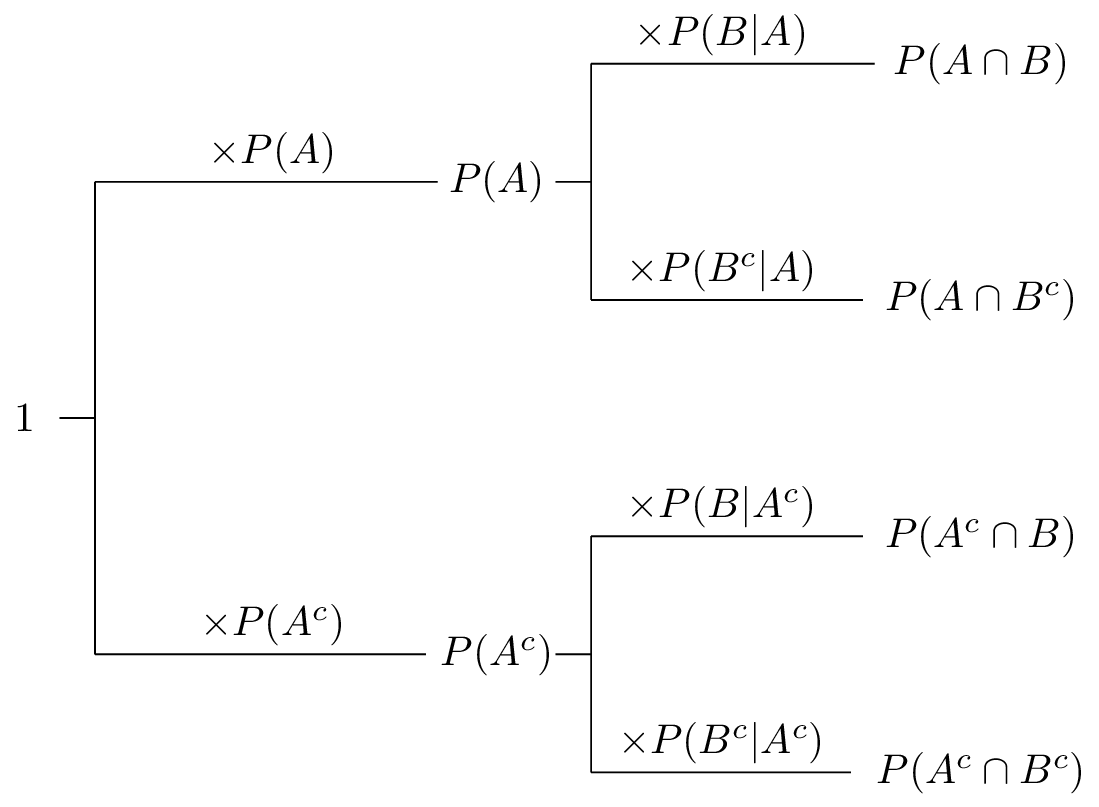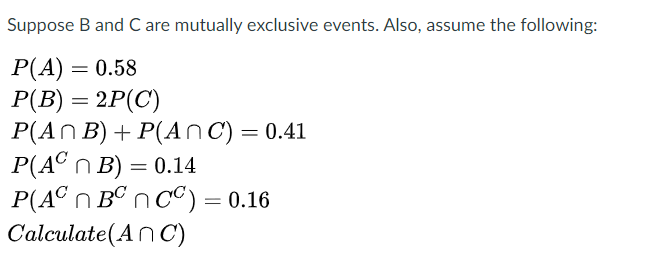SOLVED:Now, recall that in the problem set we proved that if a point P € int(AABC), then PB + PC < AB + AC State similar inequality involving the length of the

If a = Ex”,b={y',c=Ś(x" where 11.101<1; then- n=0 n=0 n=0 (A) abc = a + b + c (C) ac + bc = ab + c (B) ab + bc = ac +

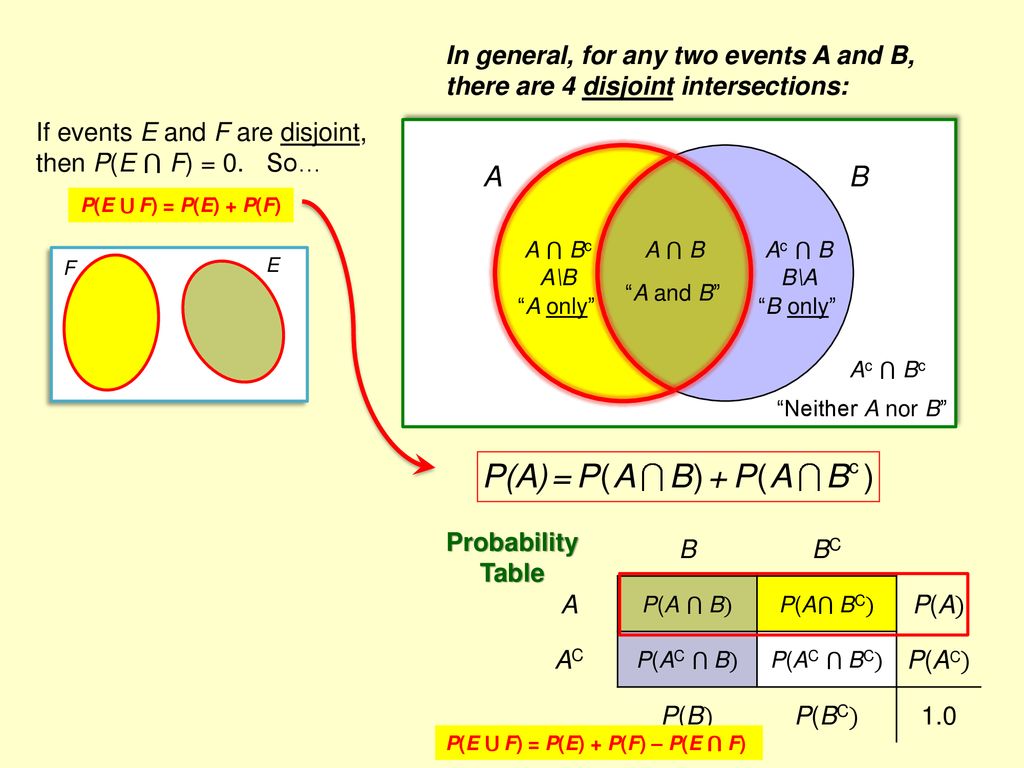
SOLVED:What is the Inclusion-Exclusion Formula with three Events A, B and C. P(ABC) = P(A) + P(B) + P(C) - P(AB) - P(AC) - P(BC) P(ABC) = P(A) + P(B) - P(AUB) -
Consider the following probabilities: P(Ac) = 0.30, P(B) = 0.60, and P(A ∩ Bc) = 0.24. a. Find P(A | - Brainly.com
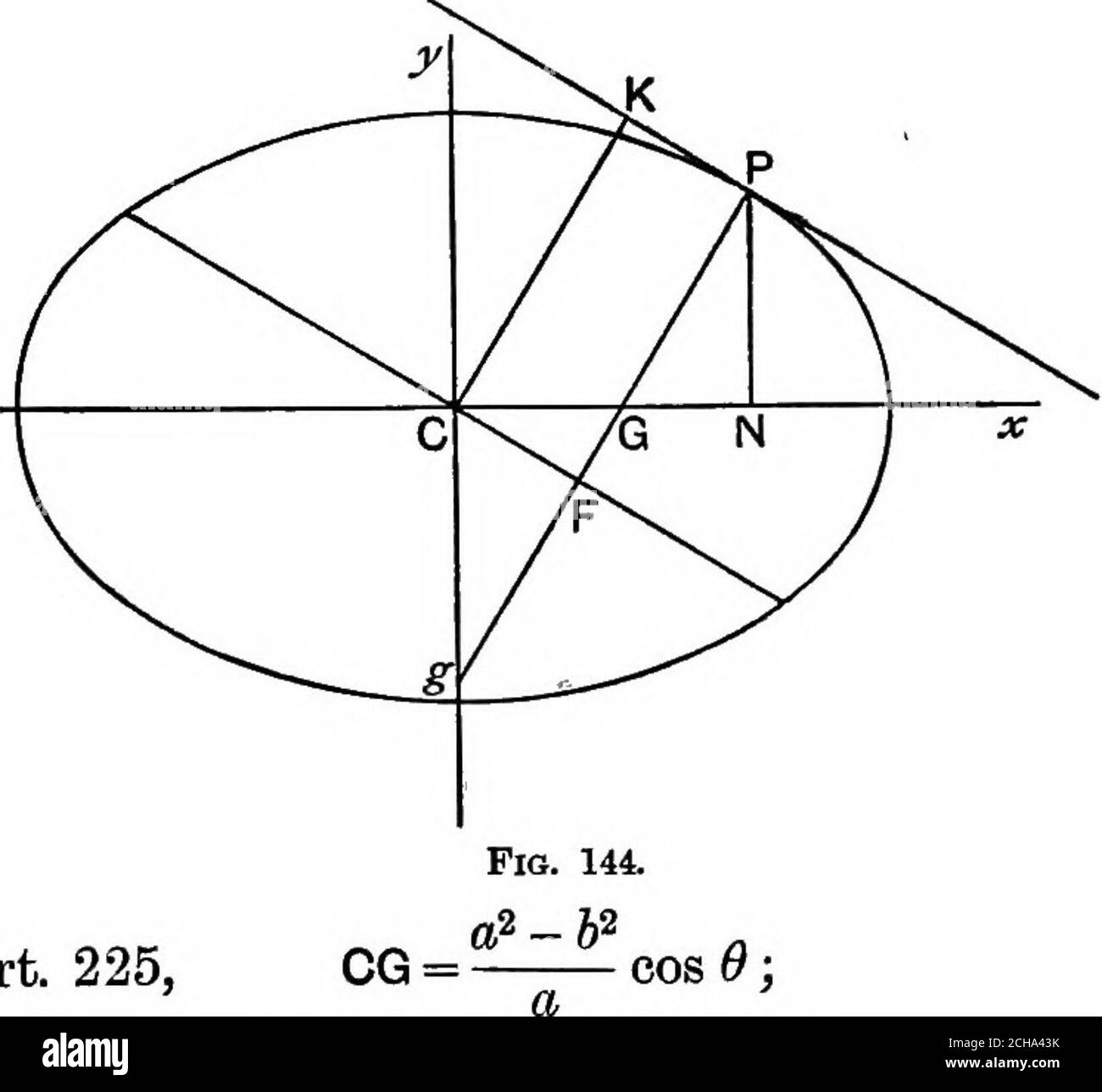
Algebraic geometry; a new treatise on analytical conic sections . Fia. 143. Draw CK perpendicular to the tangent PT, whose equation is X cos 0 y sin 6 ^ , „ . ,

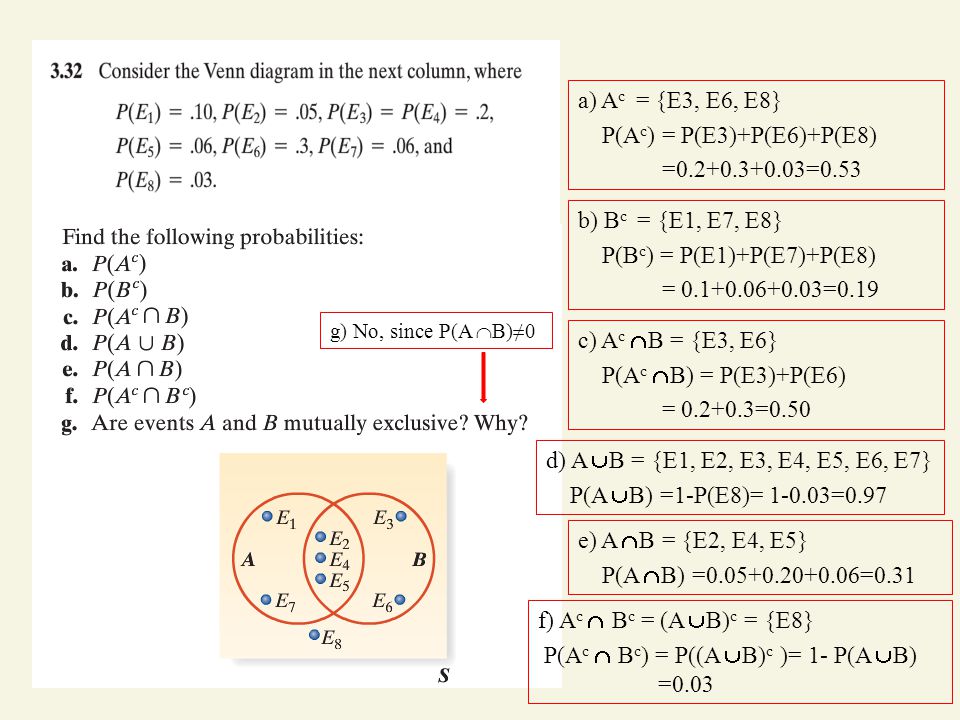
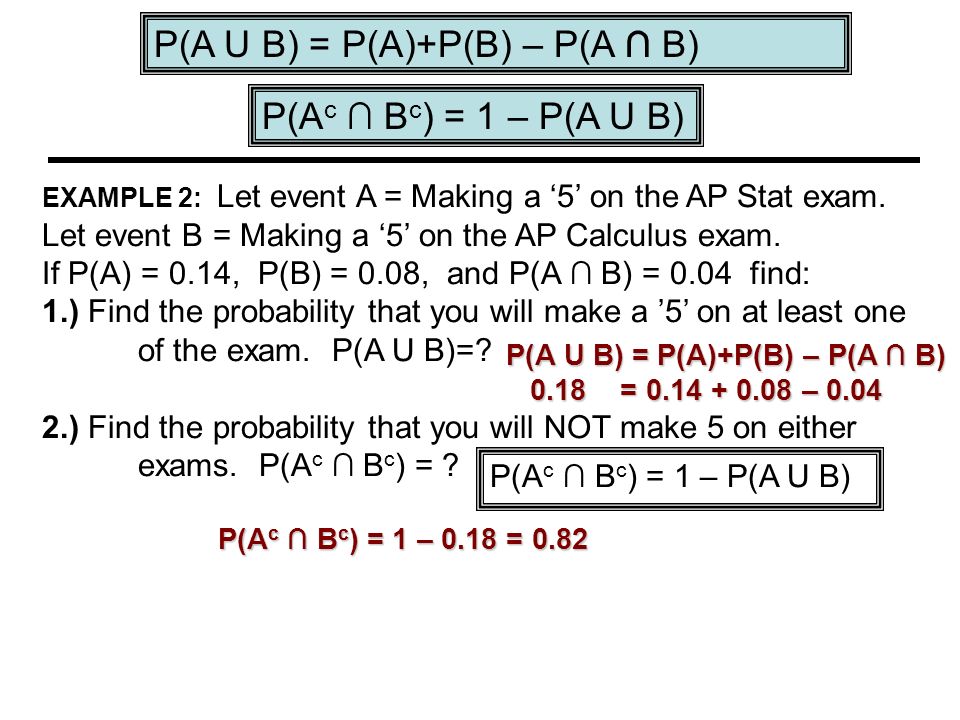
2.5 Additive Rules: Theorem 2.10: If A and B are any two events, then: P(A B)= P(A) + P(B) P(A B) Corollary 1: If A and B are mutually

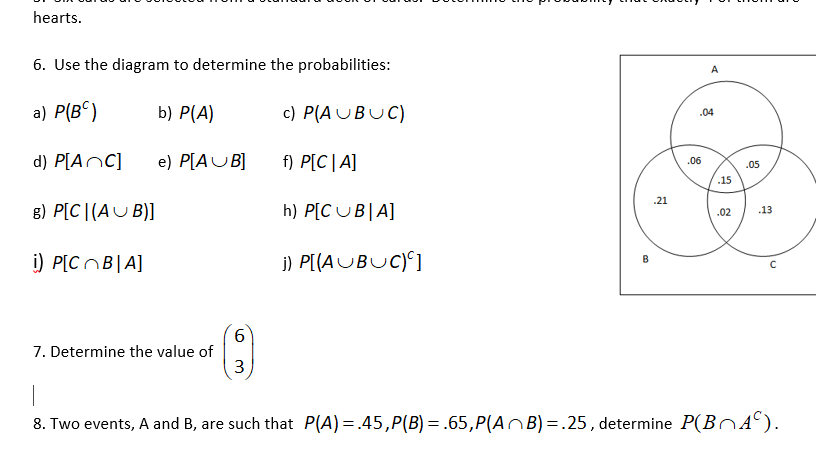
CHAPTER 3 Probability Theory Basic Definitions and Properties Conditional Probability and Independence Bayes' Formula Applications. - ppt download
📈 Point D is the in center of triangle ABC. Write an expression for the length x in terms of the - Brainly.com

P(B)P(B)P(B ) Bayes' Formula Exactly how does one event A affect the probability of another event B? 1 AP(B)P(B) prior probability posterior probability. - ppt download
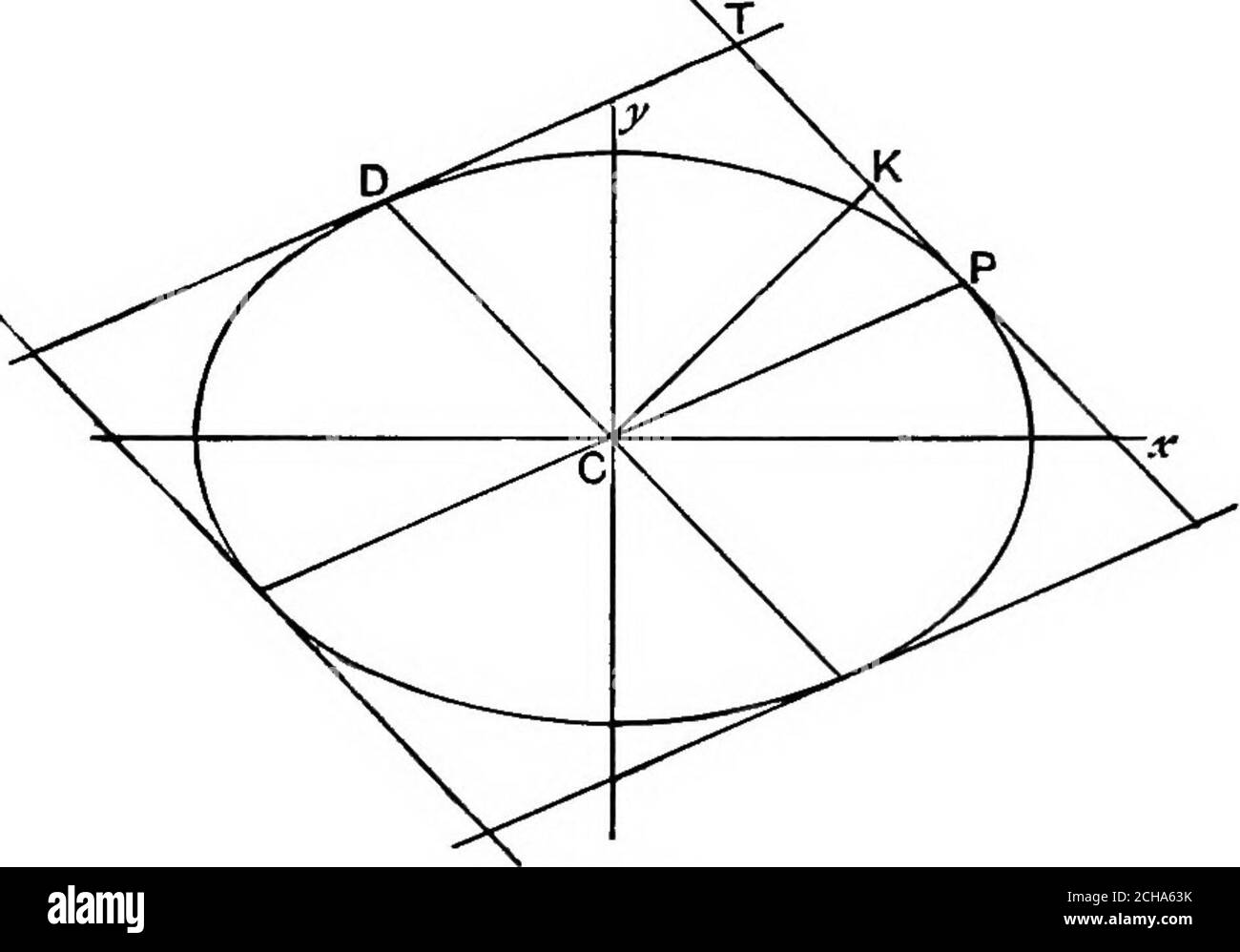
Algebraic geometry; a new treatise on analytical conic sections . 218 PROPERTIES OF THE ELLIPSE. [chap. x. 240. If CP, CD are conjugate semi-diameters, SP. SP = CD2.Let 6 be the

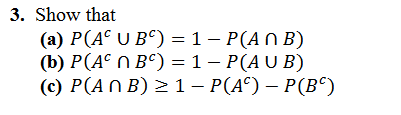





/complement-56a8fa9a5f9b58b7d0f6e9e7.jpg)